Overview of High Availability(HA)
In the fast-paced digital era, where businesses rely heavily on interconnected systems and data flow, ensuring the availability and reliability of a network is paramount. Downtime can result in significant financial losses, damage to reputation, and decreased productivity. Network High Availability (HA) is a crucial aspect of modern IT infrastructure, emphasizing the need for uninterrupted connectivity and minimal service disruptions. This article explores the concept of Network High Availability and discusses strategies, including key protocols, to achieve a resilient and robust network infrastructure.
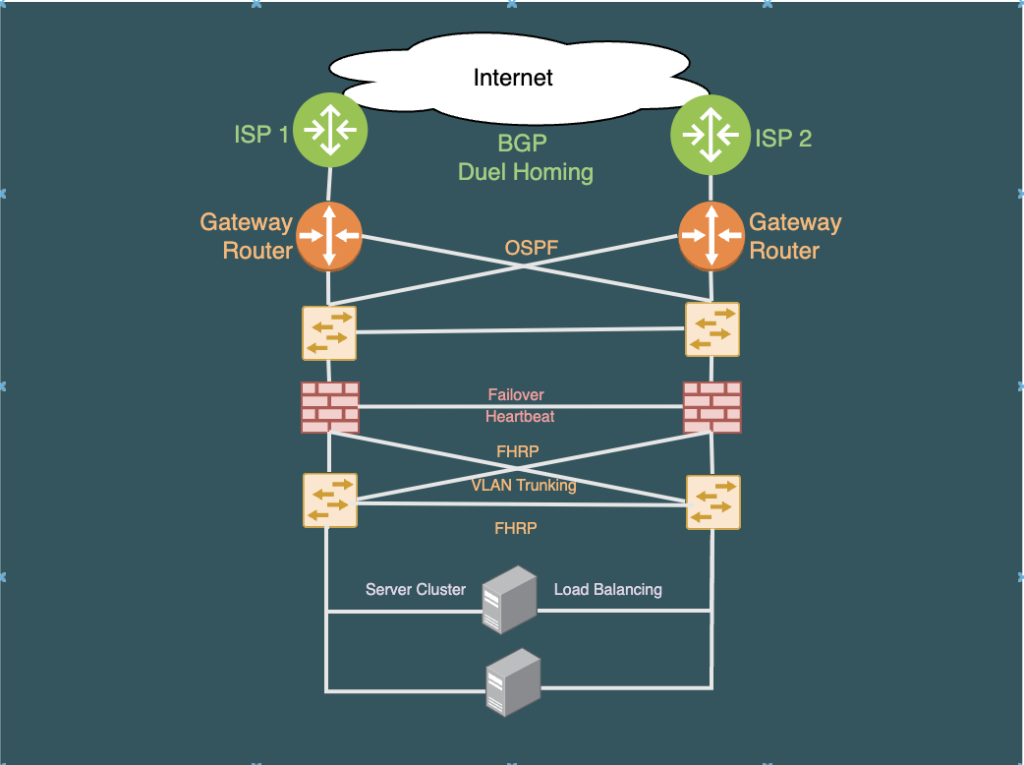
Understanding Network High Availability:
Network High Availability refers to the ability of a network to remain operational and accessible despite hardware failures, software glitches, or other unexpected disruptions. It involves implementing redundant systems and proactive measures to minimize downtime and maintain continuous service availability.
In short, a system’s high availability (HA) means it operates non-stop for a set time. HA ensures meeting agreed-upon performance levels. In IT, achieving five-nines availability (99.999%) is a challenging but widely sought standard.
Key Components of Network High Availability:
Redundant Hardware:
Deploying redundant hardware components, such as routers, switches, and servers, is fundamental to achieving high availability. By having backup devices ready to take over in the event of a failure, organizations can ensure uninterrupted service. Here’s a brief overview for each:
HA for Routers:
- Redundancy: Deploying multiple routers with synchronized configurations ensures that if one router fails, another can seamlessly take over.
- Routing Protocols: Dynamic routing protocols, such as OSPF or BGP, can be configured to quickly adapt to changes in the network topology and reroute traffic in case of a router failure.
- Virtual Router Redundancy: Using First Hop Redundancy protocols(FHRPs) like HSRP (Hot Standby Router Protocol) or VRRP (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol) allows for the creation of a virtual IP address that can failover to another router.
HA for Switches:
- Redundant Switches: Deploying redundant switches and creating link aggregation (LAG) groups can enhance network availability by providing alternative paths in case of switch failure.
- Spanning Tree Protocol (STP): Spanning Tree Protocol(STP) helps prevent loops in the network and can quickly reconfigure the topology in the event of a switch failure.
- Stacking: Some switches support stacking, where multiple switches operate as a single logical unit. If one switch fails, the others in the stack can continue functioning.
HA for Firewalls:
- Active-Active or Active-Passive Configuration: Firewalls can be set up in an active-active or active-passive mode to distribute the traffic load or provide immediate failover in case of a firewall failure.
- Stateful Failover: Firewalls can maintain the state of active connections(Stateful) so that if one firewall fails, the other can seamlessly take over without disrupting established connections.
- Clustering: Firewall clustering involves multiple firewall devices working together as a unified system, ensuring high availability and load distribution.
Load Balancing:
Load balancing distributes network traffic across multiple servers, preventing any single server from becoming a bottleneck. This not only enhances performance but also ensures that if one server fails, others can seamlessly handle the load.
Geographic Redundancy:
Organizations can achieve high availability by implementing geographic redundancy, which involves having duplicate data centers in different locations. This ensures that if one data center experiences a disaster or outage, the other can seamlessly take over, minimizing downtime.
Failover Mechanisms:
Failover mechanisms automatically redirect traffic to redundant systems or backup resources in the event of a failure. This proactive approach helps maintain continuous service without requiring manual intervention.
Network Monitoring and Automation:
Implementing robust network monitoring tools allows organizations to identify potential issues before they escalate. Automated systems can respond to these issues in real-time, ensuring quick resolution and reducing the impact of disruptions.
Strategies for Achieving Network High Availability:
Comprehensive Network Design:
A well-thought-out network design is the foundation of high availability. Consider factors such as redundancy, scalability, and fault tolerance from the outset to create a resilient architecture.
Regular Maintenance and Updates:
Keeping network equipment and software up-to-date is crucial for addressing vulnerabilities and ensuring optimal performance. Regular maintenance helps prevent system failures due to outdated components.
Disaster Recovery Planning:
Having a robust disaster recovery plan is essential for minimizing the impact of unforeseen events. This includes regularly testing backups, simulating disaster scenarios, and ensuring a clear and efficient recovery process.
Scalability:
A scalable network can adapt to changing demands and accommodate increased traffic or additional users. Scalability is essential for maintaining high availability in dynamic environments.
Network High Availability is a critical aspect of modern IT infrastructure that demands a proactive and comprehensive approach. By incorporating redundant components, implementing failover mechanisms, and adopting a resilient network design, organizations can minimize downtime, ensure continuous service availability, and protect their business operations in an ever-evolving digital landscape. Investing in high availability strategies is not just a technical consideration but a strategic imperative for businesses aiming to thrive in the digital age.




